
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines have become the backbone of modern manufacturing, from aerospace to consumer electronics. At the heart of each CNC system lies a precise movement controller, and a critical component of that controller is the gear motor. Gear motor manufacturers are responsible for designing and producing motors that deliver the torque, speed, and reliability required by CNC machines. Although they often operate behind the scenes, their product choices and innovations directly influence the performance, cost, and sustainability of industrial machining operations.
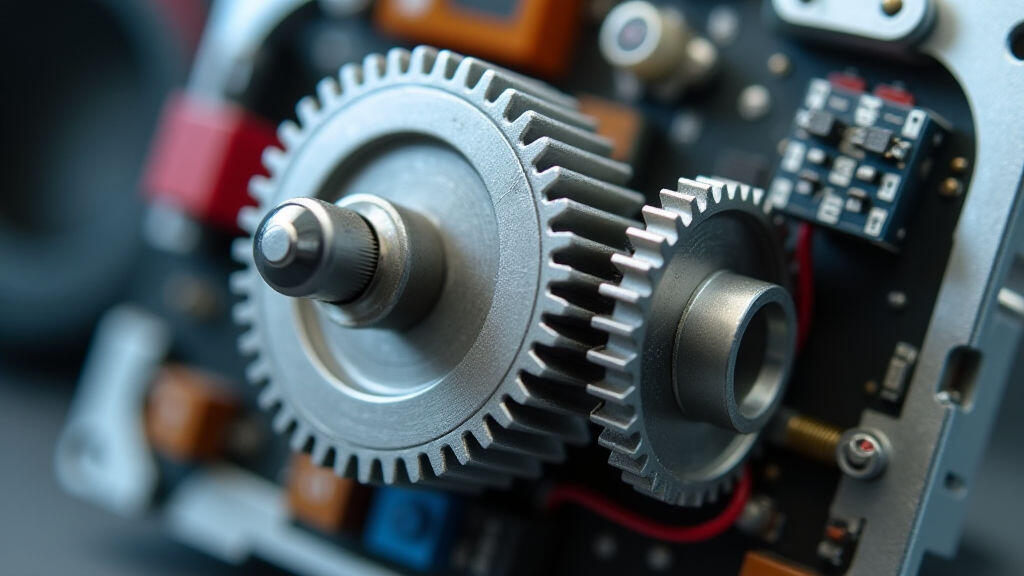
A gear motor converts electrical energy into mechanical motion, often through a series of gears that adjust speed and torque. In a CNC lathe or milling machine, these motors drive the spindle, feed axes, and tool changers. The gear reduction ratio determines how fast the spindle spins and how much pull the axes can exert. The motor’s braking capability and regenerative features also affect operator safety and energy efficiency. Therefore, the motor’s characteristics must match the tolerances, cycle times, and load demands of the specific CNC application.
Gear motor manufacturers invest heavily in research and development. They use advanced simulation tools to model gear tooth contact, reduce wear, and optimize heat dissipation. Additionally, they source high‑strength steel and apply precision machining techniques that guarantee consistent gear geometries. Quality control is another pillar; each motor must pass vibration, temperature, and endurance tests before shipment.
Adaptability is equally critical. Manufacturers offer a range of motor sizes—from small, 70 W units for hobby CNCs to 17 kW motors for industrial routers. They provide accessories such as geared couplings, encoder housings, and inline brakes, allowing OEMs to customize the motor package without redesigning the whole machine. This flexibility lets CNC builders meet diverse specifications while keeping production streamlined.
In automotive assembly plants, gear motors help maintain the high-speed spindle speeds needed for threading and drilling deep aluminum components. Here, manufacturers have introduced motors with integrated regenerative regenerative braking, which recaptures energy and lowers electricity consumption. In the aerospace sector, CNC machines that machine turbine blades demand ultra‑smooth acceleration. Companies that deliver gear motors with low harmonic distortion and tight torque ripple are the ones that win contracts.
For small and medium‑sized woodworking shops, gear motors prized for their compact size and quiet operation allow operators to set up a high‑precision CNC router on a limited footprint. A recent partnership between a local CNC sheds and a regional gear‑motor maker enabled the shop to drop operating costs by 15 % while achieving a 4 % increase in throughput, illustrating the direct economic impact of motor choice.
The market pressures for smaller, lighter, and more efficient motors are relentless. Motor manufacturers must balance these demands against cost constraints. One solution is the adoption of new materials—such as ceramic composites or titanium alloys—to replace traditional steel. However, these materials can be expensive and require specialized tooling.
Another challenge is the growing need for digital integration. CNC machines now embed telemetry and predictive maintenance software. Manufacturers respond by producing motors with built‑in sensors, like Hall‑effect speed feedback or temperature monitors, enabling real‑time diagnostics. The integration of IoT capabilities is becoming a mandatory feature rather than an optional upgrade.
Looking ahead, several trends will shape gear motor technology for CNC applications:
These innovations promise to reduce operating costs, increase machine uptime, and broaden the applications of CNC technology into new industries such as flexible manufacturing lines for bio‑materials and rapid prototyping labs.
Gear motor manufacturers play a pivotal role in the practical success of CNC machine tools. From precision engineering and quality control to adaptability and digital integration, their contributions directly affect machine performance, efficiency, and profitability. As the manufacturing landscape evolves toward higher automation, sustainability, and edge‑toward micro‑fabrication, the partnership between CNC OEMs and gear motor producers will become even more vital.
In summary, the key points that emerge are:
By acknowledging and investing in the critical role of gear motor manufacturers, the CNC industry can continue to deliver precision, speed, and innovation at the cutting edge of manufacturing.

Leave A Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fiels are marked